Navigating the world of lawnmowers can seem like a daunting task, especially when you’re faced with unexpected mechanical issues.
One critical component often overlooked is the fuel pump, a powerhouse that ensures your lawn mower runs smoothly and efficiently.
But, very few know how does a lawn mower fuel pump work for real?
That’s a question many of us have, but few can answer. Whether you’re experiencing performance issues with your mower or just curious about its inner workings, this article is your go-to guide.
The fuel pump’s role in your mower’s functionality is paramount, akin to the heart in the human body – it keeps everything running.

We’re peeling back the layers of the mysterious world of fuel pumps, demystifying their working principles, and delivering practical knowledge right to your fingertips.
With this guide, the well-kept secrets of your lawn mower’s fuel pump won’t be so secret anymore. Welcome aboard! Let’s dive in.
Table of Contents
Understanding Lawn Mower Fuel Systems
To appreciate how a lawn mower fuel pump works, we must first understand the basics of a lawn mower’s fuel system. The fuel system is the ‘circulatory system’ of your mower, ensuring that fuel reaches the engine in the right quantity at the right time.
The fuel tank serves as the gasoline reservoir for your lawn mower’s lifeblood. Connected to the tank are fuel lines, akin to our veins and arteries, that transport the fuel to where it’s needed – the carburetor.
The carburetor is like the ‘lungs’ of the system, mixing the fuel with air to create a combustible gas for the engine.

Now, not all lawnmowers have fuel pumps. Some rely on a gravity-fed fuel system. In such systems, the fuel tank is higher than the carburetor, allowing gravity to push the fuel along the lines. This simplicity makes gravity-fed systems reliable and low maintenance, but it also limits their efficiency and versatility.
On the other hand, fuel pump-equipped systems are common in larger lawnmowers and riding mowers. The fuel pump, often driven by the engine, ensures that fuel is actively drawn from the tank and delivered to the carburetor, regardless of their relative positions.
This enables a consistent fuel supply, even under demanding conditions, making these systems more versatile and suitable for powerful machines.
Grasping these basic principles is a crucial first step to understanding your lawn mower’s fuel pump operation. Let’s move on to explore different types of fuel pumps next.
Types of lawn mower fuel pumps
Fuel pumps, just like the mowers they inhabit, come in various shapes and sizes. Although their core function of transferring fuel from the tank to the carburetor is the same, their mechanisms can differ.
Primarily, lawn mower fuel pumps can be categorized into diaphragm pumps, vane pumps, and piston pumps. Let’s dive into the specifics of each.
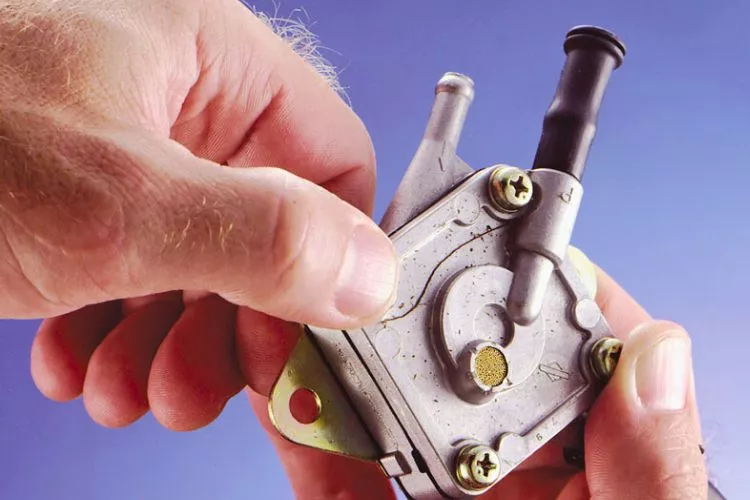

Diaphragm pumps
Diaphragm pumps are the most common type you’ll find in lawnmowers. They use a flexible rubber diaphragm that moves up and down to create a pumping action.
The movement of the diaphragm creates a vacuum, drawing fuel from the tank and pushing it toward the carburetor. They are directly operated by the mower’s engine, making them mechanically driven and not reliant on electricity.
Vane pumps
Vane pumps offer unique advantages while not as commonly found in lawn mowers as diaphragm pumps. They comprise a rotating component with protruding vanes. These vanes slide in and out, creating chambers that draw in and expel fuel as the rotor turns.
This design makes vane pumps very effective at maintaining a consistent fuel flow, even at high pressures. They are typically more robust and can handle larger fuel volumes, making them suitable for commercial-grade mowers.
Piston pumps
The least common among the trio are piston pumps. These fuel pumps use a piston that moves up and down within a cylinder to pump fuel. The downward movement of the piston creates a vacuum, drawing in fuel.
The upward movement then expels this fuel toward the carburetor. Piston pumps are generally found in high-performance or specialty mowers, as they provide high control over fuel flow and pressure.
The Role of the Fuel Pump in LawnMowers
Akin to a heart in the human body, the fuel pump has a crucial role in the functionality of your lawn mower. It ensures the seamless delivery of fuel to keep your machine running.
But where is it located, and how does it fare compared to gravity-fed systems? Let’s explore.
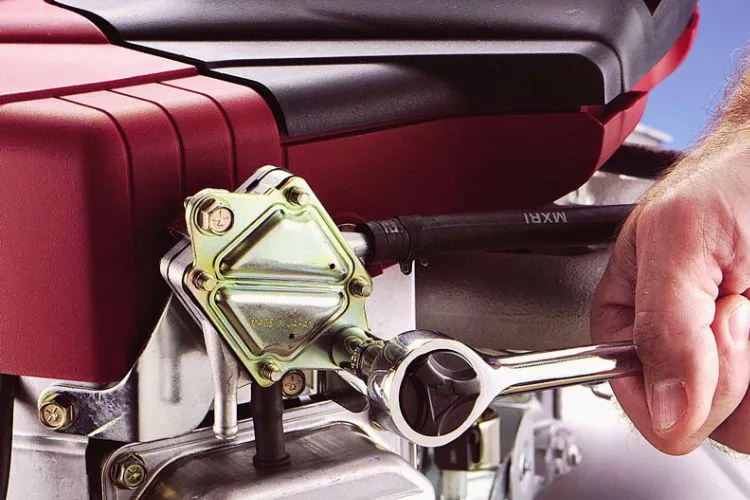

Explanation of the fuel pump’s primary function
The fuel pump’s primary role is to draw fuel from the tank and deliver it to the carburetor, a vital part of the engine where fuel mixes with air to generate combustion. The pump ensures the engine receives a steady fuel supply at the correct pressure, irrespective of the mower’s position or angle.
This consistent fuel delivery is vital for maintaining optimal engine performance and efficiency.
Fuel pump location in different types of lawnmowers
Fuel pump location can vary across lawnmowers but typically between the fuel tank and the carburetor. In riding mowers, which often have a rear-mounted fuel tank, the pump is usually located towards the front, closer to the engine.
For push mowers, the pump may be situated on the side of the engine for easy access.
Comparison of fuel pumps to gravity-fed systems
Gravity-fed systems rely on positioning the fuel tank above the carburetor, using gravity to feed fuel into the engine. While this design is simple and reliable, it’s less versatile and efficient than fuel pump systems.
Fuel pumps actively draw and deliver fuel, ensuring a consistent supply under varied conditions, angles, and loads. This makes them a better choice for larger, more powerful lawnmowers that demand greater fuel delivery control.
How Does a Lawn Mower Fuel Pump Work?
The fuel pump, small as it is, holds great responsibility within your lawn mower’s fuel system. To grasp how it accomplishes its vital task, we must understand its core components and their roles.
This knowledge enhances your understanding and can aid in troubleshooting, maintenance, and even selection when it’s time for a replacement.

Fuel pump components and design
Regardless of their type, all lawn mower fuel pumps have a few common components that collaborate to ensure smooth fuel delivery. These parts may vary slightly in design depending on whether the pump is a diaphragm, vane, or piston pump, but their roles are fairly consistent.
The Inlet and Outlet ports are the entry and exit points for fuel. The inlet draws fuel from the tank while the outlet pushes it toward the carburetor.
The Pumping Mechanism is the heart of the pump. In diaphragm pumps, the flexible rubber diaphragm moves up and down to create suction and expel fuel. Vane pumps use a rotating component with vanes to create the pumping action, while piston pumps use pistons moving within a cylinder.
Valves play a critical role in directing the flow of fuel. They allow fuel to flow in one direction – from the inlet to the outlet – and prevent it from flowing back.
The Pump Housing encases all these components. It’s typically made from durable materials like metal or high-strength plastic to withstand the pressure and corrosive nature of the fuel.
There’s also a Drive Mechanism connected to the engine in mechanical pumps (like diaphragm and some piston pumps). This mechanism, often driven by the engine’s camshaft, causes the pump’s moving parts to operate.
While these components may seem simple, their harmonious operation allows your lawn mower to traverse your lawn effortlessly.
Working principle of a mechanical fuel pump
Mechanical fuel pumps, like those found in many lawnmowers, are typically diaphragm or piston-type pumps. Depending on the specific design, these pumps are driven by the engine’s camshaft or crankshaft.
The operation of a mechanical pump begins when the camshaft or crankshaft pushes on a lever connected to the pump diaphragm or piston.
When this lever is pushed, it causes the diaphragm or piston to move, creating a vacuum within the pump. This vacuum pulls fuel in through the inlet valve from the fuel tank.
As the lever is released, the diaphragm or piston moves back to its original position, pushing the fuel out through the outlet valve and towards the carburetor. This process repeats, creating a steady flow of fuel.
Mechanical pumps are very reliable, requiring no electricity to operate. However, they can be slightly less efficient than their electric counterparts, as the pumping is directly linked to the engine’s rotations.
Working principle of an electric fuel pump
On the other hand, electric fuel pumps operate independently of the engine’s mechanical action. These pumps, typically of the vane type, are powered by the mower’s electrical system.
When power is supplied, an electric pump causes a motor within the pump to spin. This spinning motion drives a rotor with vanes that slide in and out. As the rotor spins, the vanes create chambers that change in volume.
When the chamber expands, a vacuum draws fuel in through the inlet valve. As the chamber contracts, it pushes the fuel out through the outlet valve and onto the carburetor.
This independent operation allows electric pumps to maintain constant fuel pressure, even at varying engine speeds. However, they require a stable and sufficient power supply to operate, adding a layer of complexity to the mower’s electrical system.
Whether mechanical or electric, the goal of both pump types remains the same – to ensure a smooth and consistent flow of fuel to the lawn mower’s engine.
The specific choice between these pump types often comes down to the specific design and requirements of the lawn mower itself.
Mechanical Lawn Mower Fuel Pump
With their reliable and time-proven design, mechanical fuel pumps play an indispensable role in many lawnmowers. Though these pumps might seem modest, they are the heart of your machine’s fuel system. Here, we’ll delve deeper into their operation and reveal what separates them.

A detailed explanation of the mechanical pump’s operation
The mechanical fuel pump, typically a diaphragm or piston type, relies on the lawn mower’s engine for operation. It’s mechanically driven by a lobe on the engine’s camshaft or the crankshaft. The cam or crank’s rotation translates into the pump’s diaphragm or piston’s to-and-fro motion.
When the camshaft or crankshaft pushes the lever, the diaphragm or piston within the pump is also pushed. This motion increases the pump’s internal volume, creating a vacuum that pulls open the inlet valve. The fuel from the tank, compelled by atmospheric pressure, rushes in to fill this vacuum.
Once the cam or crank’s rotation reaches the point where the lever is released, the spring brings the diaphragm or piston back to its initial position.
This return motion decreases the pump’s internal volume, creating pressure that closes the inlet valve and opens the outlet valve. Consequently, the fuel is pushed toward the carburetor.
The cyclic rotation of the camshaft or crankshaft ensures the pump’s continuous operation, maintaining a consistent fuel supply. It’s a simple yet elegant mechanism where the engine drives the fuel supply needed for operation.
Step-by-step fuel delivery process
Let’s break down the intricate ballet of the mechanical fuel pump into a clear, step-by-step process:
- Cam/Crank Pushes the Lever: As the engine runs, the rotation of the camshaft or crankshaft pushes the lever connected to the pump’s diaphragm or piston.
- Creation of Vacuum: This lever push moves the diaphragm or piston, creating a vacuum within the pump.
- Inlet Valve Opens: The vacuum opens the valve, allowing fuel to be drawn in from the tank.
- Lever Release and Fuel Push: As the cam or crank rotates. Further, it releases the lever, allowing a spring to return the diaphragm or piston to its original position. This movement pushes the fuel out.
- Outlet Valve Opens: The pressure of the fuel returning pushes open the outlet valve, sending the fuel towards the carburetor.
- Cycle Repeats: This process repeats continuously, ensuring a steady fuel flow as long as the engine runs.
Advantages and disadvantages of mechanical fuel pumps
Like any component, mechanical fuel pumps come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages
- Reliability: These pumps are incredibly durable and can last long with proper maintenance.
- Simplicity: With no need for electrical power, these pumps are simpler in design and easier to install.
- Self-Regulation: Their operation directly ties to engine speed, meaning fuel flow adjusts naturally to the engine’s needs.
Disadvantages
- Limited Pressure Regulation: Mechanical pumps may not maintain as steady pressure as electric pumps, particularly at higher engine speeds.
- Dependency on Engine: These pumps rely on the engine for operation, so any engine issue could affect the pump’s performance.
While the advantages make mechanical pumps a compelling choice, the limitations could matter depending on your lawn mowing needs. So, it’s essential to understand both mechanical and electric pumps to choose the one that best fits your situation.
Electric Lawn Mower Fuel Pump
Electric fuel pumps are the new-age counterparts to mechanical fuel pumps, bringing their advantages and challenges. With their distinct operating principles, they have carved a niche in the world of lawnmowers. Let’s dive deeper into their workings.

Detailed explanation of the electric pump’s operation
Unlike their mechanical counterparts, electric fuel pumps don’t rely on the mower’s engine. Instead, they’re powered by the mower’s electrical system and are usually located inside or near the fuel tank.
At the heart of an electric fuel pump is a DC motor. When power is applied, the motor spins a rotor equipped with sliding vanes. The rotation of the rotor forces the vanes to slide out due to centrifugal force pushing against the pump chamber’s inner walls. This action creates multiple variable-volume chambers.
A vacuum is created as the rotor spins, and the volume of these chambers increases. This vacuum opens the inlet valve, allowing fuel to be drawn into the pump from the tank.
As the rotation continues and the chamber volume decreases, pressure builds, closing the inlet valve and opening the outlet valve. The fuel is then pushed toward the carburetor.
This sequence continues as long as the pump is powered, maintaining a steady fuel supply independent of the engine speed.
This operation principle lends electric pumps certain unique advantages and limitations, which we’ll discuss in the upcoming sections, helping you make the right choice for your lawn mower.
Step-by-step fuel delivery process
Understanding the electric fuel pump’s operation becomes clearer when we break it down into distinct steps:
- Activation of the Pump: When the mower’s ignition is turned on, the electric fuel pump is activated and starts running.
- Motor Spins the Rotor: Powered by the mower’s electrical system, the pump’s DC motor spins a rotor with sliding vanes.
- Creation of Vacuum: As the rotor spins, centrifugal force slides the vanes out, creating a vacuum within the pump chamber.
- Inlet Valve Opens: The vacuum opens the valve, drawing fuel in from the tank.
- Fuel Push: As the rotor spins and the chamber volume decreases, pressure builds, pushing the fuel out.
- Outlet Valve Opens: The built-up pressure opens the outlet valve, allowing the fuel to flow toward the carburetor.
- Cycle Repeats: As long as the pump is powered, this cycle repeats, providing a steady fuel flow.
Advantages and disadvantages of electric fuel pumps
Electric fuel pumps, too, come with a unique set of advantages and drawbacks:
Advantages
- Steady Fuel Supply: Electric pumps maintain more consistent fuel pressure, especially at higher engine speeds.
- Independence from Engine Speed: As the mower’s electrical system powers them, these pumps operate independently of the engine’s speed.
- Flexibility in Location: These pumps can be installed near or inside the fuel tank, offering more flexibility.
Disadvantages
- Complexity: Electric pumps are more complex, and faults might require professional help for repair or replacement.
- Dependence on Electrical System: Their operation depends on the mower’s electrical system, so any electrical issue could affect their performance.
- Possible Overheating: If not properly designed, electric pumps can potentially overheat.
While electric pumps can offer enhanced performance but may require more maintenance, in the following sections, we’ll provide tips to keep your mower’s fuel pump, mechanical or electric, in top condition.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Lawn Mower Fuel Pumps
Regular maintenance of the fuel pump is essential to keep your lawn mower running smoothly. A well-maintained pump not only improves the efficiency of your mower but also extends its lifespan. Let’s explore some regular maintenance tips you can incorporate into your routine.

Regular maintenance tips for fuel pumps
- Regularly Check the Fuel Filter: The fuel filter is the first line of defense for your fuel pump, capturing dirt and debris before they enter the pump. Regularly check, clean, or replace it per the manufacturer’s guidelines to maintain optimal fuel flow and protect the pump.
- Inspect the Fuel Lines: Inspect the fuel lines for any signs of wear, leaks, or blockages. Cracked or damaged lines should be replaced immediately to prevent fuel leakage or pressure loss.
- Keep the Tank Clean: Dirt and rust can accumulate inside the fuel tank over time. Regular tank cleaning ensures that only clean fuel is delivered to the pump, reducing the chances of pump damage.
- Use Fresh, High-Quality Fuel: Stale or poor-quality fuel can damage the pump and the entire fuel system. Always use fresh, high-quality fuel, preferably with a fuel stabilizer, if you’re not using the mower regularly.
- Follow the Manufacturer’s Guidelines: Different mowers and fuel pumps may have specific maintenance needs. Always follow the manufacturer’s maintenance guidelines for best results.
Common issues with fuel pumps and their troubleshooting
Even with regular maintenance, fuel pumps can encounter issues. Here are some common problems and their potential solutions:
- Pump Not Delivering Fuel: If your mower isn’t getting fuel, check the fuel lines for blockages. If they’re clear, the pump might be faulty. For a mechanical pump, verify if the diaphragm isn’t damaged. Electric pumps, on the other hand, may have a motor or electrical issue.
- Lawn Mower Stalls or Surges: This could be due to inconsistent fuel supply. Check the fuel filter and lines for blockages. If they’re clean, the pump might be failing.
- Fuel Leak: This could be due to a cracked fuel line or a leaky pump. Replace any cracked lines and inspect the pump for any visible damages. If the pump is leaking, it’s best to replace it.
- Overheating (Electric Pumps): Overheating can be due to an electrical issue or poor design. Check the mower’s electrical system and consider replacing the pump if it consistently overheats.
Remember, if you’re not confident in troubleshooting, it’s best to seek professional help to avoid damaging the mower further.
Pro tips for extending the life of a fuel pump
To prolong the life of your fuel pump, consider the following tips:
- Avoid Running on Empty: Running your mower with a low fuel level can cause the pump to work harder, wearing it out faster. Try to keep the fuel tank at least half full.
- Use Fuel Stabilizer: If the mower isn’t in regular use, adding a fuel stabilizer to the tank can prevent fuel degradation, reducing the risk of clogs or damage to the pump.
- Seasonal Maintenance: Before storing your mower for the winter, consider running it dry or using a fuel stabilizer to prevent it from stale and damaging the pump.
Key Notes and Pro Tips
Keeping your lawn mower’s fuel pump in top shape isn’t rocket science, but it does require a little knowledge, attention to detail, and regular care. Here are a few key notes and tips to help you maintain your fuel pump’s health and, ultimately, the longevity of your lawn mower.

- Use High-Quality Fuel: High-quality fuel is the lifeblood of your fuel pump. It reduces the chances of sediment and debris clogging up the system, ensuring smooth operation. For example, fuel with high ethanol content might not be the best choice for your mower, as it can damage the fuel system over time.
- Regular Maintenance and Inspection: Regularly inspecting your fuel pump, fuel lines, and fuel filter can help detect minor issues before they become major. It’s easier and less expensive to replace a cracked fuel line or clean a clogged filter than to replace the entire pump.
- Safety Precautions: Always be careful when dealing with fuel. It’s highly flammable and hazardous if ingested or inhaled. When working on the fuel system, do it in a well-ventilated area, away from open flames or sparks. Use gloves and eye protection, and clean up any spills immediately.
- Clean Fuel Filters are Critical: A clean fuel filter can prevent headaches. It traps dirt and debris that could damage your fuel pump and engine. Regularly inspect, clean, or replace your fuel filter per the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Adhere to Manufacturer Guidelines: Each lawn mower and fuel pump may have specific requirements or quirks. Refer to your manufacturer’s manual or website for guidance regarding parts replacement, fuel recommendations, and maintenance schedules.
- Know Your Limits: Lawnmowers might seem straightforward, but their fuel systems can be intricate. If you’re unsure or uncomfortable with a repair, don’t hesitate to consult a professional. It’s better to get professional help than to risk further damage or compromise your safety.
Frequently Asked Questions (fAQs)
What are the signs of a failing lawn mower fuel pump?
Signs of a failing fuel pump include a lawn mower that won’t start, stalls during operation, or loses power under load. You might also notice excessive fuel consumption or fuel leaks.
Can I repair a faulty fuel pump, or should I replace it?
While some issues, like clogs, can be fixed, replacing a faulty fuel pump is generally better. This ensures optimal performance and reliability, preventing further damage to your mower’s engine.
How often should I clean or replace the fuel pump?
You should inspect your fuel pump annually, cleaning it if necessary. However, fuel pumps typically need replacement every few years, depending on usage and maintenance quality. Always refer to your manufacturer’s guidelines.
Is it essential to use a specific fuel type in my lawn mower?
Yes, it’s essential. Always use the fuel type recommended by your lawn mower’s manufacturer. Incorrect fuel can damage the fuel pump and other engine components.
Are electric fuel pumps more efficient than mechanical ones?
Both have their advantages. Electric fuel pumps can be more efficient and quieter, but they may not be as robust or easy to repair as mechanical ones. The best choice depends on your specific needs and lawn mower model.
Conclusion:
The fuel pump is pivotal in a lawn mower’s functionality, transporting fuel from the tank to the engine.
Choosing the right one for your lawn mower is crucial, whether it’s a mechanical or electric pump. Regular inspection, maintenance, and using high-quality fuel will ensure it functions optimally.
We hope that this guide has been helpful. You can read about similar topics here on our website. Check back again soon for more.

